According to IEA report, ammonia production relies on fossil fuels, contributing about 2% (8,6EJ) of the world’s overall final energy consumption. About 40% of this energy is used as raw material, supplying hydrogen to the ammonia product, whereas the rest goes as process energy, mainly for heat generation.
More sustainable solutions emitting less CO2 are emerging, such as: electrolysis, fossil-based methods lined with carbon capture and storage system (CCS) or methane pyrolysis. These methods are still more expensive than conventional ones.
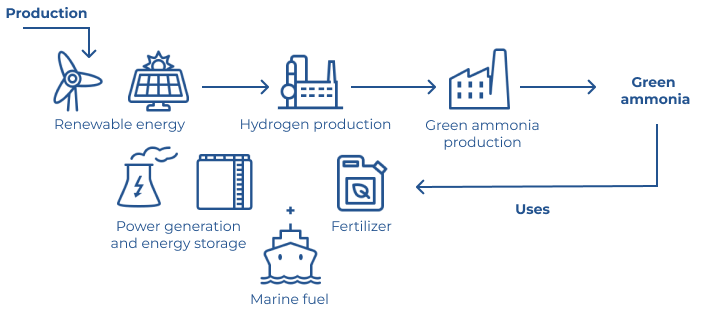
Electrochemical method uses renewable energy sources to split water into oxygen and hydrogen, which then reacts with nitrogen from air, producing green ammonia
