Fuel cell is a device converting chemical energy into electricity utilizes hydrogen and oxygen.
The outputs are water, electricity and heat. During the process, combustion doesn’t occur, limiting to zero emissions of energy generation.
H2 fuel cells, due to several advantages related to their performance characteristics and emission-free energy production, are widely applied in many sectors such as: transportation in Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs), electricity and heat generation (industrial facilities, residential) or backup power system.
This technology has advantages over conventional combustion techniques and can also reach higher efficiencies. Thus, to reach even greater efficiency, it may also be applied to power the building’s heating or cooling systems or be utilized in industrial processes.
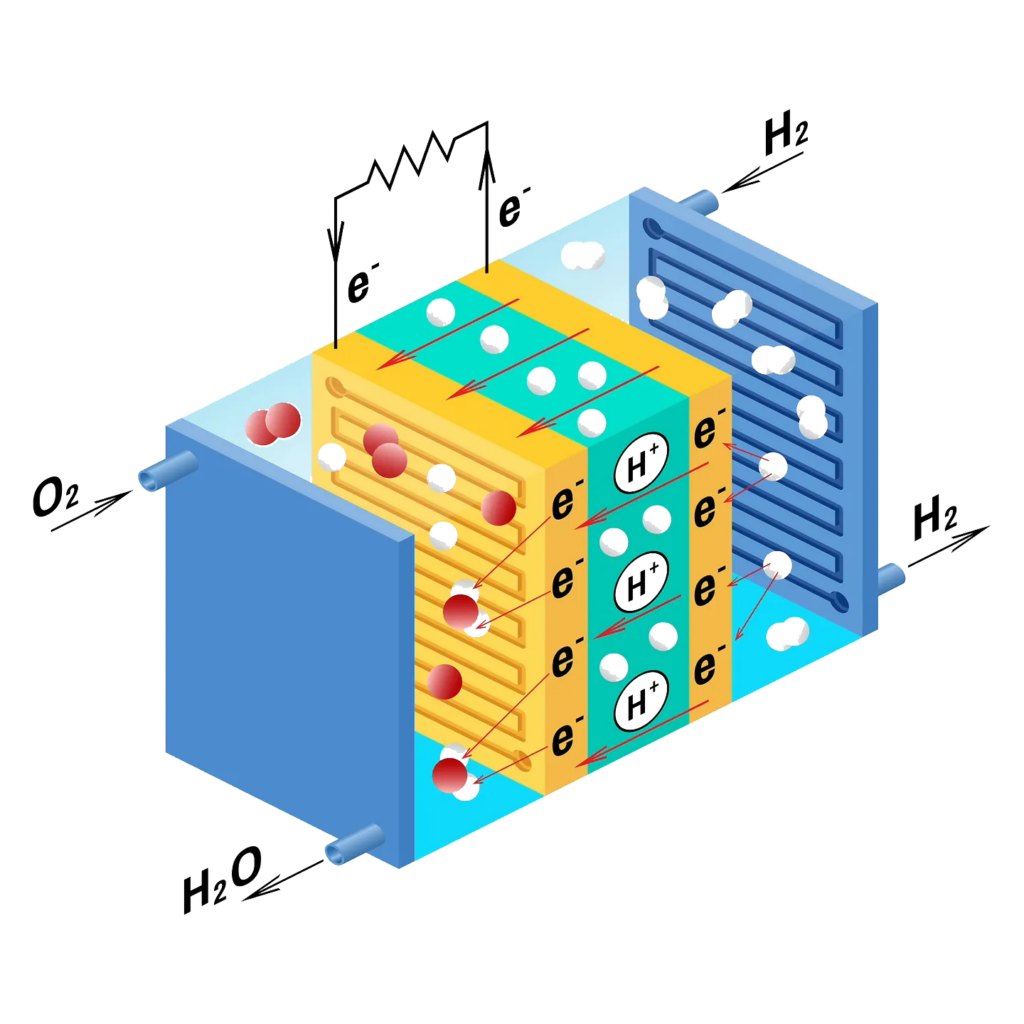
Since the technology is scalable and capable to be combined into stacks, H2 fuel cells are applicable from small devices to multi-megawatt power supply installations.
Fuel Cell’s Applications
•Light/Heavy Use Vehicles- H2 fuel cell cars are mostly available in areas, where hydrogen refueling stations already exist. Currently, there are too few stations of this type to make these cars competitive for those powered by electricity. Refueling time and driving range of hydrogen fuel for heavy-duty vehicles as buses, tracks is similar to driven by gasoline.
Furthermore, due to their predictable routes, establishing a replenishment station for such vehicles becomes more feasible over time.
•Microgrids- fuel cells could be used to store energy and combined with green energy generation facilities, to provide reliable, stable access to electricity. Through mixing energy storage by batteries and fuel cells, this ensures improved energy protection than using only one method.
•Maritime transport- replacing conventional fuel with hydrogen utilized in fuel cells is a possible solution for long distances