Oli and gas industry seeks for technological solution to maximize operational efficiencies while protect environment. One of innovative methods is nitrogen utilization by injecting it into the reservoir, as a valuable way to improve heavy oil extraction.
Well stimulation is an essential issue in the environmental topic; thus, research and development efforts are underway to develop approaches to improve production and protect environmental resources.
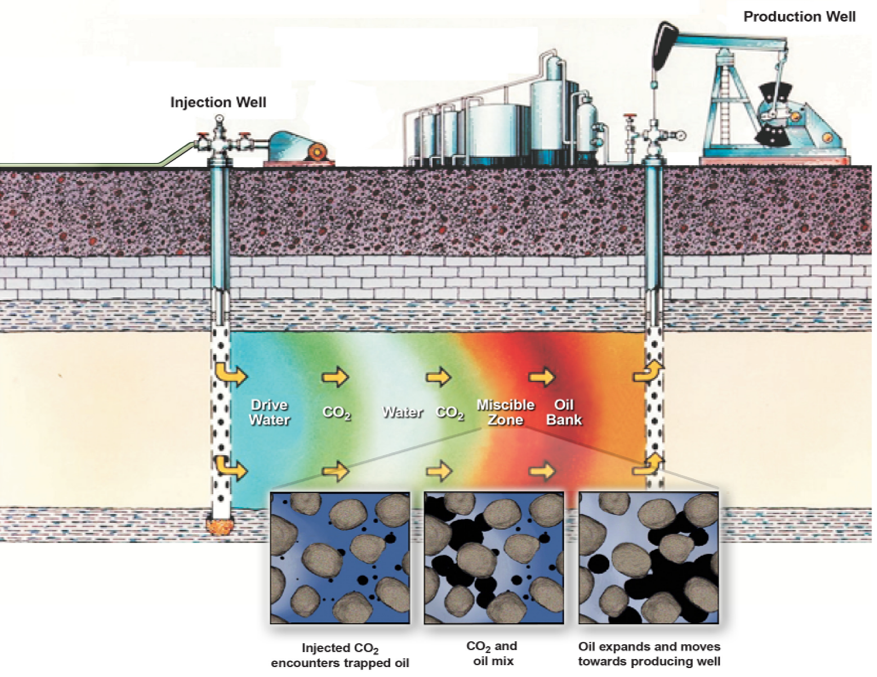
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) and Enhanced Gas Recovery (EGP) are technologies used to increase crude oil or natural gas extraction from field and various gases can be utilized for the process such as: carbon dioxide, nitrogen, steam. Among the factors that are considered in a gas selection for EOR/EGP processes are: the type of reservoir, resource availability, oil/gas properties, efficiency as well as economic aspects. Carbon dioxide can be captured from flue gas, that mainly contains N2 and CO2. Coupling Carbon Capture Utilization (CCU) technology with EOR process is favorable from the perspective of greenhouse gas emission reduction and sustainable energy sector development. In some applications, it is feasible to use a blend of CO2 and N2, that affect differently on the heavy oil and gas properties.
Nitrogen injection functions for oil and gas production:
- prevent from danger of well burning and explosion through air and hydrocarbon’s reaction in the drilling or pay zone areas.
- maintaining reservoir pressure is important with naturally occurring depressurization. It is an essential issue for the extraction operation, as the pressure must be higher than dew point pressure for the gas-liquid blend. To prevent condensation, pressure needs to rise by using pressure booster compressors performing reconstruction techniques such as displacement and cleanout operation or gas lifting.
- usage in Coiled Tubing- produced nitrogen from on-site generators flow through coiled tubing and is utilized for cleanouts, jetting or gas lifting.
- used for well completion due to nitrogen properties (low density, inertness, high pressure properties) to cementing operations, well cleaning, operation of pressure-activated components.
- equipment purging to remove water and oxygen from oil vessels and flow channels to prevent corrosion.
- Under- Balance Drilling Methods for improvement of drilling processes to reduce drill fluid weight.
- EOR nitrogen injection implemented to increase the pressure inside the reservoir to enhance oil extraction productivity.
- gas lift- nitrogen lightens the fluid and facilitates its transport to the surface.
- carrier gas for chemicals involved in the fracking process to boost oil and gas production.
Three main methods of technology can be distinguished:
Gas injection utilizes gas (such as CO2, N2, natural gas) and changes conditions inside oil/gas deposit by increase in pressure or viscosity reduction by gas dissolution, that improve the mobility of oil/gas and release to the surface
Thermal recovery through steam injection to lower the viscosity or dilute heavy oil or gas
Chemical injection involves adding polymers or surfactants to the reservoir to increase water viscosity and reduce surface tension
CO2 injection for oil and gas production:
- Carbon dioxide has the capability to reduce the viscosity of heavy crude oil and is very effective in extracting heavier hydrocarbons (up to C30).
- CO2 leads to oil swelling due to high solubility in hydrocarbons.
- Compared to methane, CO2 is more efficient in expanding the oil volume, enhancing the mobility and recovery. However, the expansion degree is influenced by the methane content in the reservoir, higher concentration of methane reduces oil swelling, due to the fact, that CO2 doesn’t completely displace the methane during contact with fluid. As a result, the presence of methane limits the effectiveness of CO2.
- In a flood process, CO2 facilitates the oil vaporization and extraction, achieves miscibility between 100 and 300 bar, effectively decreasing water density. Furthermore, it lowers density contrast between oil and water, consequently reducing the potential for gravitational separation. Moreover, it diminishes the oil and water surface tension, leading to a more effective displacement process-s.
- CO2 injection is optimal solution for the reservoir with maximum temperature of 80-120⁰C, depth between 1500 and 3500 m, and low oil viscosity of 0-100 mPa·s.